Laboratory Infrastructure
The ACS Lab was inaugurated on 19th September, 2014 at the Academic Block (Vallabh College Campus), Indian Institute of Technology Mandi, India. On 26th March, 2016, the lab moved to Bamboo Block B (B-08) on Institute’s main campus at Kamand. Lab members come from different fields which include computer engineering, electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, civil engineering, and humanities and social sciences. The ACS Lab contains a high-speed network of several computing machines for experimentation and modeling. Mentioned below is some of the laboratory infrastructure at ACS Lab.
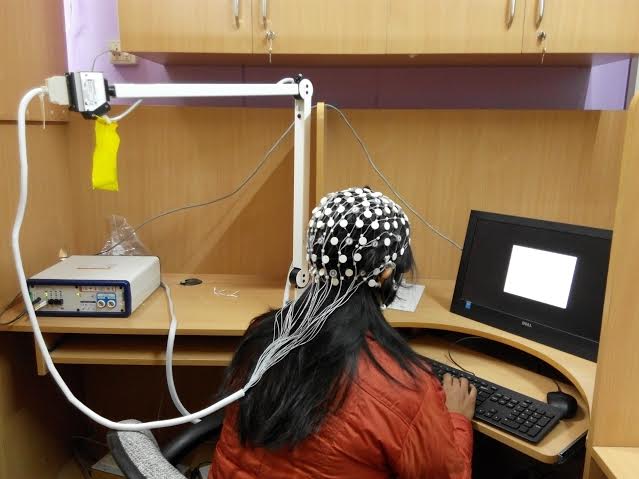
32-channel EEG/ERP system (Geodesic EEG System 405)
Emotiv® 14-channel EEG/ERP headset
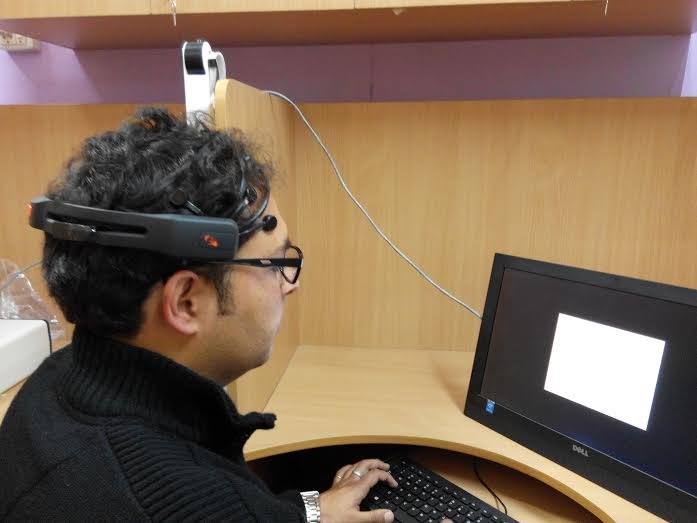

Leap Motion And Leap Motion Controller
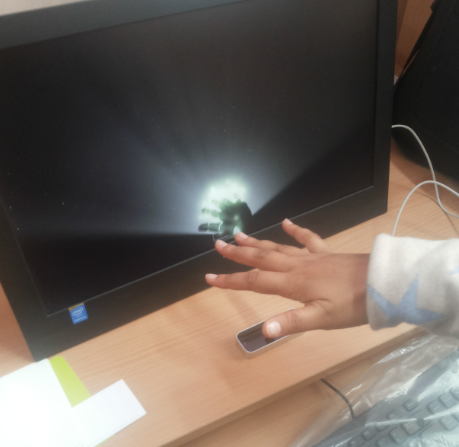

Tobii® EyeX Eye Tracker

Oculus Rift Headset

Google Cardboard headset

Xbox Kinect

Logitech® Driving Simulator

Contec Oximeter

HP® Workstation

Contact Us!
Phone
Dr. Varun Dutt
+91-1905-267184
+91-1905-267009
varun@iitmandi.ac.in
Address
Applied Cognitive Science Laboratory
School of Computing and Electrical Engineering
School of Humanities and Social Science
IIT Mandi, Parashar Road, Tehsil Sadar Kamand
Himachal Pradesh 175005
India